Solutions & Solubility
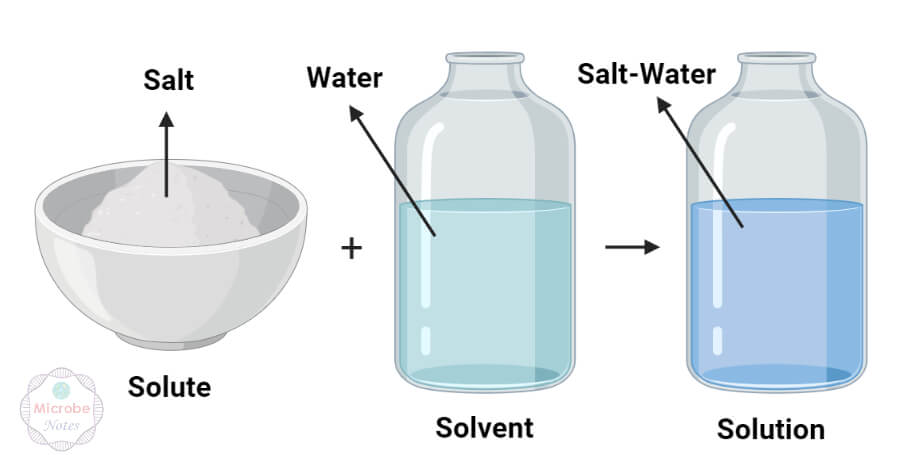
Solute
A solute is a substance that is added to a solvent to form a solution.
Examples of solutes:
– Salt
– Sugar
– Carbon dioxide
Solvent
A substance that dissolves the solute particles during the formation of a solution.
Examples of solvents:
Water
SOLUBILITY
The amount of a given solute that can be dissolved in a certain amount of solvent at a particular temperature or pressure (for gases).
Solubility is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a solvent at equilibrium.
Saturated solution
A saturated solution contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute at a given temperature in the presence of undissolved solute.
In a saturated solution, the processes of dissolving and recrystallizing are in equilibrium: Solute (undissolved) = Solute (dissolved)
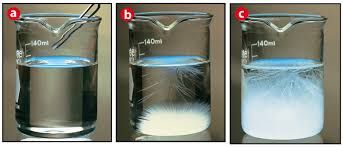
A solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute is called an unsaturated solution.
Supersaturated Solution
A supersaturated solution contains more than the equilibrium amount of dissolved solute. These solutions are unstable. The excess solute can be readily precipitated.
